For your convenience, all the maps from Series 2 gathered together on one PDF:
Uncategorized
Review: The Witcher: Blood Origin
So it turns out The Witcher is better without The Witcher.
A long time ago I watched the first 3 or 4 episodes of The Witcher and never warmed to it. I liked the monster fights. But the production varied in quality from ‘dripping with Gothic atmosphere’ to ‘just plain tacky.’
The prequel series Blood Origin caught my attention by accident over the Christmas. Now, since watching it I’ve tried to read a review or two to find out why so many people (but not everyone) hated it. This one from Polygon was largely incomprehensible to me. It’s not just that I disagreed; I did not understand what the criteria were by which the series was being judged.
To my eyes, it was not a series that undermined the precious canon or a mess of a story which invited me to pick it apart to explain how it failed. It was a pulp swords-and-sorcery adventure which looked and sounded good, which had a cast of fun, engaging characters, which was focused and disciplined at a tight four episodes. The class war elements set up in the first episode with the rabble-rousing song ‘The Black Rose’ paid off in spades at the end when a revolution was part of the final showdown.
That review from Polygon says: ‘There’s a class conflict that keeps getting hinted at through a song Élie [sic] is famous for, but there’s never much consideration of what that actually means, in-universe, beyond “lower-class folks are hungrier than their elite counterparts.”’
I said of Andor that I didn’t need it to be a Ken Loach film. Well… I don’t need a three-hour fantasy story even to be Andor, let alone Ken Loach. The class war element was not at all simplistic – it was just focused and coherent.
One last quote from that review: ‘When Élie promises Scían the chance to reclaim the sacred sword of her people, it’s introduced in the conversation with no explanation for how Élie would’ve even known it was gone.’
Not only did that not bother me, it didn’t strike me as a thing which might conceivably bother anyone. Éile has lived in this world all her life and presumably knows about various things. If she has shoelaces (I can’t remember) she probably learned to tie them at some point in her life, but we don’t need a flashback explaining this.
Who first came up with the trope of making Elves speak the Queen’s English? In this, the elves have Welsh, Irish and other regional accents. If that’s a feature of The Witcher (I can’t remember) then good for The Witcher. Tolkien-variety elves are a mythical reflection of Celtic peoples as seen through Anglo-Saxon eyes.
They got the tone just right. It doesn’t take itself too seriously, but then it doesn’t let silly banter undermine the serious moments either. After just two and a half episodes, we get a sequence where the seven adventurers sit down and have a party. That strikes me as a difficult thing to pull off; the writers have got to warm the viewers up to the characters and the characters to each other. Blood Origin pulled that off.
The cast was uniquely diverse. I say ‘uniquely’ because off the top of my head I can’t think of another TV series or movie in the genre that does such a good job of reflecting the diversity of our species in its cast.
I felt it could have gone on just a bit longer, another episode or two, and that the promised ‘Conjunction of the Spheres’ ended up being skimmed over. Neither of these things was a deal-breaker for me; in fact I was relieved that it wasn’t a sprawling, incoherent mess that was too busy setting up hypothetical future seasons to tell its own story. I could forgive it for erring in the other direction.
Finally and crucially, I was relieved that platinum-blonde Solid Snake was nowhere to be seen. I don’t want to criticise The Witcher too much because that would be churlish in this context. Geralt of Rivia has an iconic look, I suppose, but I never found him interesting in my limited exposure to the show. His absence leaves a lot of room for other characters to throw their weight around.
Anyone familiar with the stuff I write about here on The 1919 Review might suspect that I only enjoyed this show because it had two things I liked: class struggle and Irish stuff (‘Inis Dubh’ means ‘Black Island’). But if they hadn’t been there, I would still have enjoyed it: I read a lot of science fiction and fantasy, and I appreciate a punchy, well-crafted tale of sorcery and adventure with strong characters and a vulgar edge. Blood Origin is all that.
Review: The Pull of the Stars by Emma Donoghue
Emma Donoghue’s The Pull of the Stars begins like a movie sequence full of long tracking shots, following a nurse on her commute through the dark of early-morning Dublin streets in the autumn of 1918.
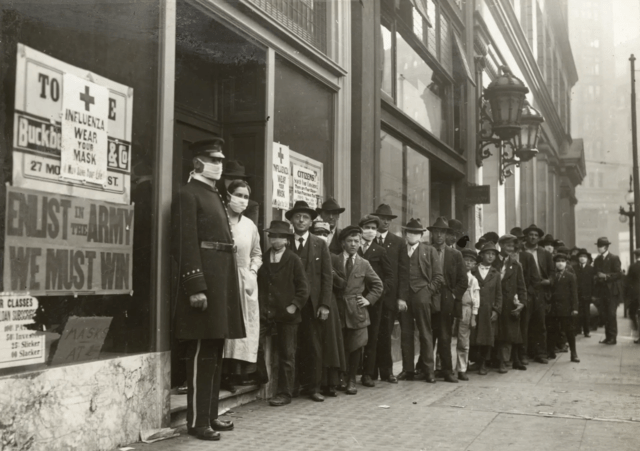
There are masked men spraying the gutters with disinfectant, children assembling at the train station for evacuation to the country, fear on the tram at every cough and spit: this is the height of the ‘Spanish Influenza’ pandemic.
After what she calls ‘the grippe,’ the next item in order of relevance to our narrator, Nurse Julia, is the ongoing First World War. It’s in its last few weeks, but she does not dare to hope that rumours of mutinies and moves toward peace are true. The war is as inescapable as the pandemic in the way it shows up in a wealth of details in this everyday experience.
The struggle for independence is a distant third, or perhaps it’s even further down the list of priorities for Julia. She passes the burnt-out ruins of O’Connell Street which still haven’t been rebuilt after the 1916 Easter Rising, which she dismisses in her mind as an act of crazy violence by a handful of extremists (Later she says to a rebel supporter, with icy understatement, ‘I got some experience with gunshot wounds during that week.’)
More relevant than the national question is the patriarchal influence of the Catholic Church: it is considered unseemly for Julia to cycle to the church-run hospital where she works.
It could be argued that the author is laying it on thick with the sheer amount of historically relevant things jostling for attention in every paragraph of Julia’s commute. But it’s authentic: these were extraordinary times and history was not something you could escape, least of all in the routine of everyday life. Reconstructing this extraordinary and forgotten moment is an important feat.
Later we will learn that Julia has never heard of Thomas Ashe, the Irish Republican who died on hunger strike in 1917. We never see her reading a newspaper, so it’s believable that the whole thing would have escaped her attention. And it’s not just plausible, it’s kind of refreshing. There was other stuff going on.
Getting caught up in the work
When Julia arrives at her hospital she and the reader get caught up in her work. Before you know it, you’re a third of the way through the book and you care deeply about the current condition of each of her patients. She’s looking after maternity patients who also have the virus; she has to keep these women and their babies alive. It’s one thing after another. We are swept up in the technical (and gruesome) details of the craft and the personalities which populate the cramped room.
When a volunteer arrived to help Julia, I was so invested in the work that I felt a rush of crazy gratitude toward this fictional character.
This character is Bridie Sweeney, and we will learn a lot about her over the next three days. And when we know Bridie’s story, we will question whether it’s enough for Julia simply to save the lives of these women and their infants. Many of them are destined for the orphanages, laundries, mother and baby homes andindustrial schools, a vast half-hidden Gulag which Bridie refers to as ‘The Pipe.’ Meanwhile infants in Dublin have a worse chance of surviving than soldiers in the battles of the ongoing war.
Changing attitude to the rebels
There is the gradual intrusion of Dr Kathleen Lynn, a real-life character. She is at first a troubling rumour – the hospital is scraping the bottom of the barrel and hiring a terrorist! – then a reassuring, compassionate and professional presence in the makeshift maternity/fever ward. We can see Julia, not consciously but no less obviously, changing in her attitude toward Lynn and the other ‘terrorists’ who led the 1916 Rising. People are dying every day anyway, argues Lynn – not from gunshot wounds, but from poverty and squalor caused by capitalism.
Lynn is perhaps a too-perfect character, who always has a clever and compassionate answer to every challenge. But it’s not like she’s Pearse or Connolly; she’s an underrated figure and long overdue a tribute in fiction.
A Covid novel
Like Oisín Fagan’s Nobber, The Pull of the Stars is a book about a past pandemic which was written just before Covid. The writer was not thinking of lockdowns, masks, jabs and Zoom calls. But the mind of the reader is dominated by comparisons.
What we see in the book is a lot worse than what Irish people have gone through in recent years, for the simple reason that in 1918-1919 there were apparently no half-way serious public health measures. There was no vaccine. Bad and all as our health service is today, there was no health system worthy of the name in 1918.
The attitude of the state is conveyed in poster slogans. One says: ‘Would they be dead if they’d stayed in bed?’ As Julia notes, it’s much more difficult for working-class people to stay in bed for days. Another says that ‘THE GENERAL WEAKENING OF NERVE-POWER KNOWN AS WAR-WEARINESS HAS OPENED THE DOOR TO CONTAGION. DEFEATISTS ARE THE ALLIES OF DISEASE.’
But there was always a strong element of that in public health messaging during Covid as well – scolding people instead of helping them, demanding sacrifices instead of providing basic supports. The hospital in The Pull of the Stars– overcrowded, understaffed; every nook and cranny turned into a ward, the canteen banished to the basement – will be drearily familiar to many who worked during Covid.

Midwifery
Earlier I said the opening was cinematic, but later on The Pull of the Stars reminds us what movies can’t do but novels can. It is unflinching in its treatment of the details of nursing and midwifery – there is no misguided delicacy, in other words. You won’t see this in Call the Midwife or Emma Willis: Delivering Babies. TV won’t show this stuff, and actually it couldn’t even if it tried.
I don’t know enough about the history of obstetrics to say how accurate it all is, but nothing rang false to me.
Changes
Equally convincing is the way Julia changes. The extreme circumstances, along with a whirlwind experience of love and loss, move her deeply. Lynn’s socialist politics appear to have a catalysing effect. At the end of the novel Julia makes a radical decision which puts her on a collision course with the nuns.
The real reckoning in the novel is not with the pandemic. The ‘Spanish’ Flu merely shines a revealing light on empire, patriarchy, capitalism and the church. Above all else, it’s the horrors of ‘The Pipe’ that bring about change in Julia’s character. I’d bet that the Tuam Babies scandal was closer to the mind of the writer than the Bird Flu or SARS.
There is some implausibility in the ending. But Donoghue has succeeded in convincing us that this was a historical moment rich in implausibility. This is a rich and strange and terrible time when people might do extraordinary things. The choice Julia makes is moreover justified on a thematic and story level – a miracle that is ‘earned’ by tragic losses earlier.
This is a short novel and, I found, a gripping one. I’m interested in this period in history so I drank in all the detail. More importantly, Donoghue’s narrative of a midwife caring for a handful of pregnant invalids is somehow more exciting than any epic action scene I’ve read lately.
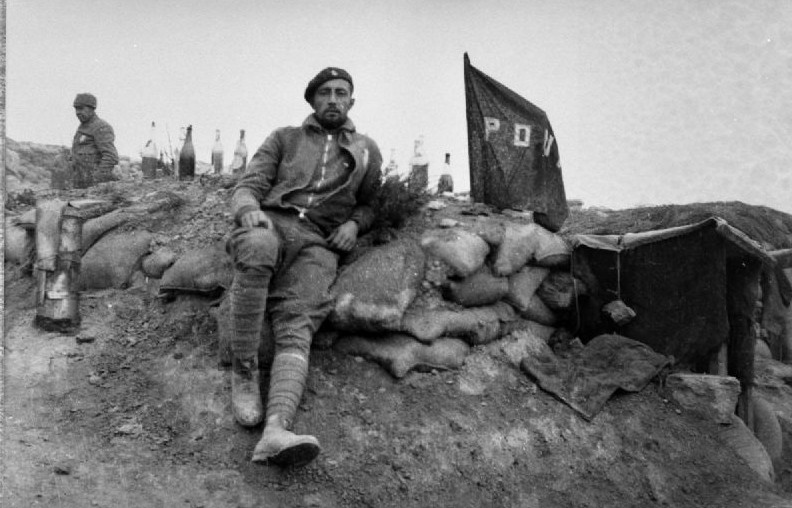
18: The Chelyabinsk Trap
On the Eastern Front in July 1919, the White regime of Admiral Kolchak was reeling after its armies were driven out of the Ural Mountains. But the Siberian Whites made an audacious throw of the dice, triggering one of the largest battles of the Civil War.
To set the scene for us, here is the diary of General Alexei Pavlovich Budberg, a minister in Kolchak’s government. He recorded his horror and frustration as things fell apart:
July 19th 1919:
Head is spinning from work […] To our disadvantage, the Red Army soldiers at the front were given the strictest order not to touch the population and to pay for everything taken […] The admiral gave the same orders […] but with us all this remains a written paper, and with the Reds it is reinforced by the immediate execution of the guilty.
July 20th 1919:
[…] self-seekers and speculators are white with fear and flee to the east; tickets for express trains are sold with a premium of 15-18 thousand rubles per ticket.
July 22nd 1919:
The Ministry of Railways receives from the front very sad information about the outrages and arbitrariness committed during the evacuation by various commanding atamans and privileged rear units and organizations; all this greatly complicates the hard work of evacuation […]

Hints of a planned White counter-attack do not give Budberg any relief. On the contrary, he was filled with foreboding:
July 23rd 1919:
Something mysterious is happening at headquarters: operational reports have been temporarily suspended…
In the rear, uprisings are growing; since their areas are marked on a 40-verst map with red dots, their gradual spread begins to look like a rapidly progressing rash.
July 24th 1919:
The mystery […] has been aggravated: to all my questions I receive a mysterious answer that soon everything will be resolved and that very big events will take place that will drastically change the whole situation.
July 25th 1919:
Only today did I learn at headquarters that [General] Lebedev, with the cooperation of [General] Sakharov, wrested from the admiral consent to some complex offensive operation in the Chelyabinsk region, promising to completely eliminate the Reds […]
Undoubtedly, this is Lebedev’s crazy bet to save his faltering career and to prove his military genius; it is obvious that everything is thought out and arranged together with another strategic baby Sakharov, who also yearns for the glory of the great commander.
Both ambitious people obviously do not understand what they are doing; after all, the whole fate of the Siberian white movement is put on their crazy card, because if we fail, there is no longer salvation for us and we will hardly be able to restore our military strength…
Chelyabinsk
The city of Chelyabinsk lies amid a cluster of lakes, a few hours by rail east of where the Ural Mountains fall away to the plains. It can be regarded as ground zero of the Russian Civil War: it was there that a brawl between Czechs and Hungarians led to the revolt of the Czechoslovak Legion.
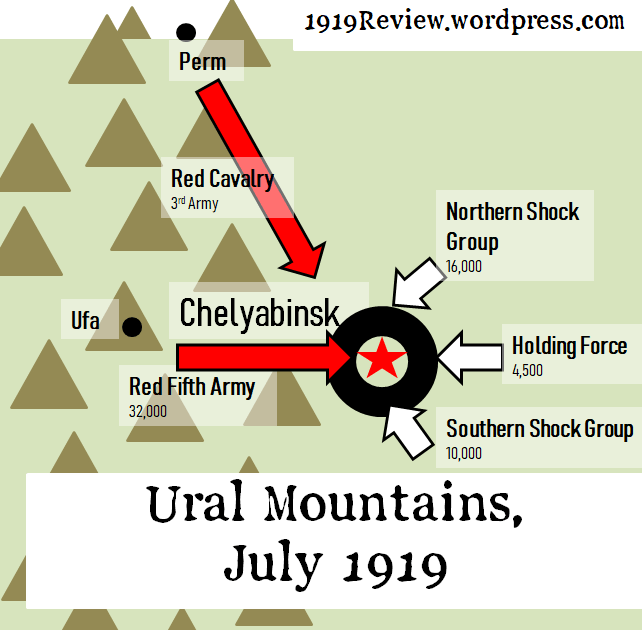
At the end of July the Red Fifth Army came down from the Mountains into the lake country. This was the same Fifth Army that had held the line at Sviyazhsk and then crossed the Volga to seize Kazan. Trotsky and Vacietis counselled caution and rest for Eastern Army Group after it drove back the White Spring Offensive. But the new commander-in-chief, the military specialist Kamenev, argued for a hot pursuit of the Whites right into the heart of Siberia. So far Kamenev had been vindicated. The same Chinese Reds, led by Fu I-Cheng, who had lost Perm the year before had recaptured it. The Red commander Frunze had taken Ufa after a terrible and bloody fight with Kappel.[i]
Now the Fifth Army was advancing on Chelyabinsk. But Kolchak, on the advice of his young generals Lebedev and Sakharov, had decided to turn the city into an elaborate trap. The Reds would be allowed to seize the city – then encircled in it, and destroyed.
On July 24th a workers’ uprising began in the city. It was led by an underground Bolshevik organisation that had suffered under the counterintelligence operations of the ‘very cruel’ Colonel Sorochinsky. The Red Fifth Army hurried to the aid of the rebels, and linked up with them. Railway employees sabotaged the White defence: they derailed one armoured train and diverted another into a dead end. The city fell, and the Reds captured many rifles and machine-guns. Morale was good, energy high: Red detachments at once began scouting and advancing out from the city through the suburbs and villages.
But to the north, south and east, White shock groups and formations were closing in on the city to encircle and destroy the Fifth Army.
Let’s pause and get a proper sense of scale. The last time this series zoomed in on a particular battle, that of Kazan, it was easy enough to visualise. In an arena measuring forty kilometres by twenty, there were between ten and twenty thousand soldiers per side.
The Battle of Chelyabinsk compels us to think bigger, on a scale of at least 80 square kilometres.
There were 32,000 rifles and swords in the Red Fifth Army. On the side of the Whites, there were around 30,000 as well: the Northern shock group numbered 16,000, the southern shock group 10,000, and there were 4,500 to the east holding the line between the two.

The Trap
Let’s zoom in on one of those fighters, a White cavalry officer named Egorov.
At four in the morning of June 25th Egorov was waiting with his regiment at a crossroads near one of the several lakes north of Chelyabinsk. Egorov’s Mikhailovsky Regiment consisted of 150 mounted soldiers – ‘rather motley,’ by his own admission, old and young, mostly infantrymen mounted rather than ‘real’ cavalry – along with soldiers on foot.
They were ordered to gather here before seizing the village of Dolgoderevenskaya, north of Chelyabinsk.
Egorov and his men were still stinging from the postscript added to their orders: ‘I advise the regiment commander, Colonel Egorov, to abandon this time the usual delay…’
Adding insult to injury, the Mikhailov Regiment was on time. They were waiting in the early hours of the morning for the Kama Division to show up.
‘To the right and left I hear voices: “Why wait for the Kamtsy?.. Move!.. Enough of the Reds!”’
Egorov decided it was time. The regiment sneaked up close to the village. A local Cossack boy told them there were many Reds in the village, but a lot of them were asleep.
The attack began. White cavalry broke through the outskirts of the village without a shot being fired, and before most of the Reds were awake the White cavalry had dispersed all over the streets while infantry attacked from the west.
‘And only after that,’ writes Egorov, ‘the first rifle shots were heard.’
He was watching from a nearby hillside. The rifle fire intensified, and the sound of the Russian war-cry, ‘Urrah!’ came to him. After an hour of fighting, the Reds fled to the next village.
As Egorov entered the village he heard someone shout: ‘Mister Colonel! Trophies!’
His men were looting what the enemy had left behind: gramophones and field-kitchens. Egorov reckoned the Reds had, in their turn, taken the gramophones from the houses of priests and merchants.
But the Whites got carried away in the celebrations. The Reds counter-attacked and caught them unawares. Fortunately for Egorov, the Kamtsy arrived – the stragglers Egorov had not bothered to wait for – and they had artillery. By three in the afternoon the Reds had been driven back again. Egorov and his cavalry mounted up, and this time pursued them, and drove them out of the next village as well. The Reds began to retreat all along the front.
Egorov’s assistant, a Tatar, had taken a bullet in the arm during the day’s fighting. He was unperturbed. That night at dinner he drank heartily. Then he excused himself, went out into the hall, and removed the bullet with a penknife.
These battles were part of the advance of the northern shock group. It was very successful; it reached the Yekaterinburg-Chelyabinsk railway line, cutting off the Fifth Army and threatening it from the rear.
On 27 July the southern shock group advanced. Its purpose was to link up with the northern group, completing the encirclement. The southern group was commanded by Colonel Kappel, who had led the Whites at Kazan. Kappel was a relic of the late Komuch government and its ‘People’s Army,’ now serving Kolchak and the Whites. There were others present at Chelyabinsk for whom Komuch had served as a Red-to-White pipeline or gateway drug. The workers’ militia of Izhevsk were there, going into battle to the sound of accordions.
Meanwhile the 4,500 White Guards in the middle advanced west into the outskirts of Chelyabinsk.
Another White veteran recalled: ‘On one of the days, apparently on the 27th or 28th […] we found ourselves 3-4 versts from Chelyabinsk and were about to have dinner there.’
He and Egorov and Kappel had good reasons to feel confident. Many would have believed that just as Denikin was advancing in South Russia, they were about to turn the tide in the east.

Resistance
According to the plan, the Reds should have been panicking and falling to pieces by now. Generals Sakharov and Lebedev were young officers who had learned most of what they knew during the period of the Czechoslovak Revolt of 1918. They had led irregular detachments against untrained Red Guards.
But these Reds in Chelyabinsk were made of something else. They held firm. Kappel engaged in heavy battles to the south of the city, but his forces could not break through.
The Chelyabinsk revolutionary committee put out a call, and 8,000 miners and other workers joined the defence, arms in hand. 4,500 others joined work detachments, building defences and supporting the troops. The centre group of Whites could not advance further, and got bogged down in the outskirts.
Why couldn’t the Whites make any headway? We noted in a previous episode that they had raised two divisions of young conscripts. These forces had not even been trained when they were flung into the battle at Chelyabinsk. To encircle an enemy army would have been a challenge at the best of times. The White officers were ordered to spring the trap with personnel who did not know what they were doing.
In Russia, soldiers with rifles are called streltsi, literally ‘shooters.’ One veteran wrote to the Chelyabinsk local newspaper in the 1970s, recalling his days as an officer leading White streltsi:
I was a participant in the battles near Chelyabinsk on July 25-31, 1919, not in the Red Army, but in the White Army, in […] the 22nd Zlatoust regiment of Ural mountain shooters, which they practically were not [sic], since […] they were not even trained at all how to shoot.
During the battle, up to 80% of the 13th Siberian rifle division went over to the Reds. They surrendered in their thousands, bearing US Remington rifles and wearing British uniforms.
It wasn’t just the new conscripts. In the headlong retreat since May, divisions had winnowed to regiments, regiments to, in one case, a ragged group numbering only seventy. Typhus had raged through the White units. Many of the replacements were young Tatars, like Egorov’s friend. Many of these couldn’t speak Russian.
Kappel’s Volga Corps had taken a battering in recent months. Instead of getting time to recover, they, like the new recruits, were thrown into battle.

On the other side, the Red Fifth Army was experienced and energetic. And they had a political backbone: in the 27th Division alone there were 600 Communist Party members.
But the fighting was fierce. According to one source there were 15,000 Red and 5,000 White casualties.[iii] According to other sources, the Whites lost 4,500 killed and wounded, while 8,000 or even 15,000 were captured, and the Red casualties numbered 2,900.
The Reds held on in the centre and south, then reinforced the vulnerable north. They built up a shock group of their own and between July 29th and August 1st defeated five enemy regiments north of the city. I assume this involved sweeping through the villages Egorov and co had taken nearly a week earlier. Perhaps the gramophones changed hands again.
Cavalry units from the Third Red Army at Perm were hurrying to the aid of Chelyabinsk and threatened the Whites’ northern shock group. The Izhevsk militia was sent to meet them, but the Izhevtsi suffered heavy losses at the village of Muslyumovo. The northern shock group had itself suffered a series of shocks. Its position was untenable.
Back in Omsk, General Budberg was asked by Kolchak what he thought of the Chelyabinsk Operation.
July 31st
I reported to him that I think that now it is necessary to immediately stop it and order to do everything possible to withdraw the troops involved in it with the least damage to them.
The admiral was silent, but asked to speed up the dinner, then went into the office to Zhanen, where he signed a telegram to Lebedev about the retreat; he is very gloomy and anxious.
August 1st
Everything connected with the Chelyabinsk adventure, and most importantly, my powerlessness to stop it and prevent all its consequences, led me to the decision to ask the admiral to dismiss me from my post, and if it is impossible to give [me] a place to the front, then to [accept my resignation].
Budberg’s request was refused, and so he was forced to around Omsk as an agonised and impotent witness to further disaster.
Red advance
From August 1st the Reds were on the offensive. The White retreat eastward grew more chaotic.
Many in the White camp had warned against the Chelyabinsk operation. They favoured instead a defensive strategy: digging in behind the Ishim and Tobol rivers and buying time to train up the new units. After ‘the trap failed to close’[iv] at Chelyabinsk, the White armies were demoralised and sorely depleted. Digging in was less feasible than before, but even more urgent.
The Siberian Whites were not finished all at once. In late July the Siberian Cossack host joined Kolchak’s cause – too late to help at Chelyabinsk, but just in time to give Kolchak and others a false hope in a renewed offensive strategy. Nonetheless the Red advance across Siberia was indeed delayed by serious battles with the Cossacks and on the defence lines of the rivers.
Crisis in White Siberia
But the Battle of Chelyabinsk is not so much a story of Red victory as one of White defeat. That defeat is interesting because in every way it was symptomatic of the crisis that was developing in Kolchak’s Siberia.
Behind White lines there reigned a regime of corruption and terror that exceeds the most lurid caricatures of the Red side. Untrained and demoralised men sent to fight the partisans would torment the farmers, burn villages, loot, torture and kill. Bodies hung from the telegraph-poles along the Trans-Siberian railway.[v] Further east under Semyonov and Ungern, as we have seen, things were even worse.

Budberg lamented how among the middle and wealthy classes of the towns everyone felt free to criticise, but never lifted a finger to help in any practical way. It seemed everyone was out for themselves, embezzling without the slightest shame. In the White capital city, Omsk, many wealthy and well-educated people were concentrated. But the poor could not afford to eat and attempts by the state to provide the most basic relief or public services always somehow ended in a dead-end of bungling and embezzling.
The Czechs, whose revolt had given birth to the Eastern Front at Chelyabinsk the year before, were growing disgusted with the White cause, and becoming almost as much of a pain to the Whites in 1919 as they had been to the Reds in 1918. The first stirrings of mutiny were already evident. And in the woods the partisan forces were growing and developing. Meanwhile the Socialist Revolutionary Party were raising their heads again, active both among the partisans and the Czechs. They were the ghost at Kolchak’s feast: he had jailed them after his coup in November 1918, and shot many after the Omsk revolt of December.
Kolchak’s army had come to resemble, in miniature, the Tsarist army of 1917 – in June there had been cases of the men shooting their officers and changing sides. No wonder – the officers had brought back Tsarist practises such as flogging men and striking them in the face. In October, a mass of newly-raised conscripts was sent to the front, and melted away without a trace. Of 800,000 ‘eaters’, only one in ten were fighters; many soldiers travelled with their families in tow. They looted the locals to feed themselves. Some of their supply trains stretched out to 1,000 carts.
‘These were not military units,’ said one disgusted officer, ‘but some kind of Tatar horde.’[vi] Many of those fighting and dying were actually Tatars, so this is a fine example of all the cultural sensitivity we would expect from a White officer.
The battle at Chelyabinsk showed that a spectacular role reversal had taken place. In 1918, the Whites were the professionals, the elite soldiers, and the Reds were the undisciplined rabble. But the rabble had developed into an army. And on the other hand, when the Whites tried to move from elite detachments and all-officer companies to a mass army, they degenerated into a rabble. Their best units were better than the Reds, but their worst units were far worse. The Whites of 1919 were incomparably stronger on paper. But – and this was especially true in Siberia – they had the worst of both worlds. Compared to the early Red Guard formations, they had all the raggedness and all the indiscipline, but none of the political motivation.
Many on the White side noticed the change in the aspect of the Reds. ‘A White leader who visited Tobolsk after it was briefly recaptured was impressed at reports of how well the Reds had behaved.’ And General Budberg wrote that ‘we are not up against the sovdepy and Red Guard rabble of last year but a regular Red Army.’[vii] ‘Sovdep’ was a White nickname for the Reds, based on the words ‘Soviet’ and ‘Deputy.’ Budberg considered the Reds’ battle plans to be plodding and basic. But even basic plans were, in his view, better than none, or than the ‘too clever by half’ manoeuvres of Lebedev and Sakharov.
The Chelyabinsk battle also revealed another key weakness of the White Guards. On November 4th Kolchak complained that his army recruited from among ‘Bolshevik-minded elements’ who at the first opportunity ‘crossed over to the Red side.’ As a result, officers ‘refused to dilute their units’ with new recruits! ‘We had to recruit with great selectiveness, while the enemy freely used local manpower which was favourable to him.’[viii] In other words, the Whites were hindered by the small fact that most people didn’t want to fight for them, and favoured the Reds (even in relatively conservative Siberia).
It is true, as Beevor says (p 344), that ‘A civil war was not an election […] because the vast majority of people wanted to stay out of trouble.’ It is not possible to ascertain the will of the people by ballot in the middle of a civil war. We have to go with cruder measures, such as asking which side could reliably recruit thousands and which side could reliably recruit millions. Judging by this crude but immensely significant measure, the people preferred the Reds to the Whites.
Often the story of the Civil War is one of cruelty and dashed hopes. But the victory at Chelyabinsk was one worthy of a popular revolution. The workers’ rebellion at Chelyabinsk and the participation of thousands of volunteers in the battle underlines this democratic aspect.
The Battle of Chelyabinsk showed how Fifth Army had developed from the semi-irregular force that fought at Kazan into a professional army. But most of Siberia still lay before it, and far behind to the west, Tsaritsyn and Kharkiv had already fallen. Denikin’s advance on Moscow was already well under way.
Go to Revolution Under Siege Archive
[i] Beevor, 323
[ii] Smele, 113
[iii] Mawdsley, 210
[iv] Mawdsley, 210
[v] Beevor, 238
[vi] Mawdsley, p 211
[vii] Mawdsley, 208
[viii] Mawdsley, 214
The diaries of General Budberg came from militera.lib.ru_
In addition, this episode could not have been written without a collection of sources compiled by an internet user named igor_verh on https://forum.axishistory.com/viewtopic.php?t=192991. (The name at first raised alarm bells for me but the site’s description says it is apolitical. Its focus seems to be wargaming).
The sources are as follows, copied and pasted from the post:
http://war1960.narod.ru/civilwar/chelybinsk1919-1.html
http://www.book-chel.ru/ind.php?what=card&id=4415
http://www.hrono.ru/sobyt/1900sob/1919chelyab.php
http://kadry.viperson.ru/data/pressa/3/ … 983007.txt
http://chelyabinsk.rfn.ru/rnews.html?id=97133
http://city.is74.ru/forum/showthread.php?t=43062&page=2
Memories of M.V. Belyushin – the former ensign of 22th Zlatoust mountain riflemen regiment about battle near Chelyabinsk in the summer of 1919:
http://east-front.narod.ru/memo/belyushin.htm
The downfall of the 13th Siberian Rifle Division in the battles near Chelyabinsk in 1919:
http://east-front.narod.ru/memo/meybom1.htm
Sanchuk P. “Chelyabinsk operation in summer 1919”, publication in magazine “War and Revolution”, № 11, 1930:
http://elan-kazak.ru/sites/default/file … chuk/1.pdf
17: Anarchy in the Ukraine
This episode tells how the warlord Grigoriev in Ukraine led a bloody revolt against the Soviet power. The episode will then describe his fatal showdown with the anarchist Nestor Makhno.
‘Anarchy’ means ‘without rulers,’ not ‘without order’ or ‘without laws.’ Still the word is often used to signify chaos. Here we can sidestep the controversy, because the word applies in both senses to Ukraine in 1919. The title of this post refers to the Anarchist army which operated in Ukraine at this time, ‘a singing army which moved in carts – a machine-gun and an accordion in each cart – under black banners.’[i] But it also refers to the state of chaos and violence which prevailed in many parts of the country and under flags of all colours – not just black. By May, ‘villages turned in on themselves’ for protection, ‘while armed bands roamed the countryside, led by warlords.’[ii]

Grigoriev in Odesa
When last this series covered events in the great port city of Odesa, it was in a state of utter chaos with the evacuation of Allied interventionists. Reds were already marching in.
A Red commander reported to Moscow that the city had been taken ‘exclusively’ by the forces of the charismatic partisan leader Nikifor Grigoriev. These fighters had shown ‘revolutionary stamina’ and Grigoriev had led from the front: he had two horses shot from under him, and bullet holes in his uniform. But on the day before the fall of Odesa he was taking a well-earned break: he spent the day drinking from a bucket of wine and listening to the regimental band.[iii]

Odesa was a wealthy city, and in 1919 its warehouses were bursting with the goods and equipment which the Allies had left behind in the chaos of their evacuation. Grigoriev made himself a kingly giver of gifts in relation to all this loot – for example, 30,000 rifles were apparently sent to the villages of the Kherson region. There is also a story that he looted hundreds of kilograms of gold from the Odesa State Bank.[iv]
The local Communists – those who had fraternised with the French in the cafés – celebrated the liberation. But very soon the city’s revolutionary committee was addressing complaints to the warlord about his claiming of the loot.
‘… I occupied Odessa,’ he later told Makhno, ‘from where the Jewish Revolutionary Committee appeared. They came to my headquarters … They began to demand that [I obey them], that the lads stop beating the Jews. And you know, people on the campaign were torn, worn out, and there are a lot of Jewish speculators in the city […] I took the city, therefore, it is mine, and then the Revolutionary Committee crawled out of the underground and stood in my way, talking about submission. When I attacked, there wasn’t a single member of the Revolutionary Committee with me, but now, you see, they decided to be the boss.’
He was just boasting. But the eyes of the Soviet government were not blind to the problems Grigoriev might present. He had switched sides three times already. He gave lip-service to communism but anti-Semitic slogans were current among his supporters. Yet he had driven the Allied interventionists right out of Ukraine. The Soviet government awarded him the Order of the Red Banner for this triumph.
After ten days in Odesa, local communists were already demanding that Grigoriev be arrested. A bloody clash appeared inevitable. But Grigoriev and his forces withdrew to the villages near Kropvynitsi (then known as Elizavetgrad). To give you a sense of the distance, today that’s a five-hour drive inland.
Grigoriev in Budapest?
As summer approached, the Soviet laid plans to have Grigoriev carry the banner of the October Revolution to the very heart of Europe. The Hungarian Soviet Republic was isolated and under attack. Grigoriev’s force was, on paper, a short distance from Hungary: just charge right through Transnistria and Romania (Or through Poland and Slovakia), and boom, there you are. But the problems are so obvious that one is forced to wonder what the hell the Soviet leaders were thinking. Grigoriev was not exactly the ideal ambassador for communism, and once he’d seized Budapest he might well change sides again. He was a partisan leader, not a rounded-out military genius, and such an ambitious attack was likely beyond his capabilities. Maybe the Soviet government was desperate (We have to help the Hungarian comrades, no matter the cost or the risks!) or maybe they were cynical (this might keep Grigoriev out of trouble – and with any luck he won’t come back alive) or maybe some mixture of the two was at work. At the very least Grigoriev might divert Romanian forces and take the pressure off Soviet Hungary.
For better or for worse, probably for better, it never happened. Grigoriev switched sides again. He had turned from Rada to Hetman and back again, before turning to the Reds. Now he struck out on his own, backed by tens of thousands of armed soldiers and by a large part of the Ukrainian farming classes.
Grigoriev in Revolt
When is an ataman officially in revolt? When does he cross the line? He always has plausible deniability, because he is not fully in control of his forces. Many Communists, such as Antonov-Ovseenko, were in denial about his revolt at first.
By his own account, his revolt developed organically as a response to overbearing communists: ‘My troops could not stand it and began to beat the [Cheka] themselves and chase the commissars. All my statements to Rakovsky and Antonov ended only with the dispatch of commissars. [Eventually] I just kicked them out the door.’
From the communists’ perspective, Grigoriev had been operating as a law unto himself for too long. Soviet government officials were allowed no authority on his territory, and many communists were quietly murdered. One commissar ordered to go to strike a deal with Grigoriev refused, citing poor health. But it is obvious the commissar was in fear for his life, with good reason.
On May 1st a Grigoriev armoured train celebrated International Workers’ Day by firing explosive shells into Kropvynitsi. Over the next week, anti-Jewish and anti-communist pogroms swept through the local area. On May 7th a Red commander threatened to attack Grigoriev if the pogroms did not stop. On the same day several Chekists boarded Grigoriev’s armoured train and tried to arrest him. They were themselves captured and later shot.
On May 8th (one month after literally riding into Odesa on a white horse), Grigoriev published a manifesto titled the ‘First Universal.’ It was no longer possible to doubt his intentions.
It was a forceful appeal to the Ukrainian farmer. It began by recounting the horrors of the Great War and German occupation before moving on to those of the Civil War. It blames the ‘Muscovites’ and those ‘from the land where Christ was crucified.’
‘Those who promise you a bright future exploit you! They fight you with weapons in their hands, take your bread, requisition your cattle and assure you that all this is for the benefit of the people. Hard-working, holy man of God! Look at your calloused hands, look: all around – untruth, lies and insults […] You are the Feeder of the World, but you are a slave.’
He called for soviets but without communists, along with representative bodies where the majority of seats would be reserved for Ukrainians. He demanded that the Ukrainian Soviet government ‘leave us’ and summoned each village to send fighters to Kyiv and to Kharkiv – with weapons, and if there were no weapons to hand, with pitchforks.
By May 10th there was no longer any pretense or hesitation. Grigoriev’s army, which was between 16,000 and 20,000-strong, had risen up against Soviet Ukraine, with armed columns speeding out in all directions from Kropyvnitsi.
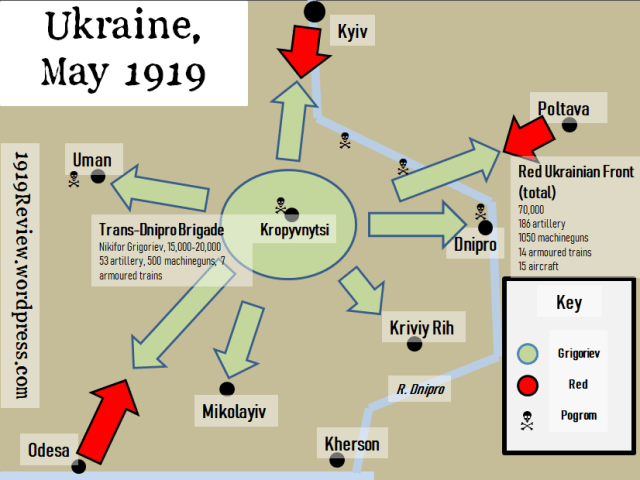
What did this revolt look like? A Grigorievite column would ride into town by horse or by train, or a Red garrison would declare for Grigoriev; usually a combination of the two – for example at Kremenchug, Chigirin, Zolotonosha and Cherkasy. In Pavlograd the Red Army soldiers revolted of their own accord. In Dnipro anarchists and sailors went over to Grigoriev and handed him the city. In all, about 8,000 Red Army soldiers went over to Grigoriev.
Soviet officials would be shot. Jews would be robbed, violated, killed. Prisons would be opened. In Kropyvnitsi, epicentre of the revolt, we see all of the above on May 15th: a pogrom which killed 3-4,000 Jews and several hundred Russians. Some of the murderers were those who had deserted from the Red Army. In other towns and villages, we see hundreds killed here, thousands killed there. According to Savchenko: ‘The commanders of the Grigorievites in Cherkassy urged each insurgent to kill at least 15 Jews. An eyewitness writes: “There is no street in Cherkassy where families have not been killed. Russians and Jews were dying… indiscriminately.”’
Dnipro was briefly recaptured by the Reds, and they executed one out of every ten ten of the captured Grigorievites. But in short order the other nine out of ten revolted in prison, and again took over the city.
What was the scope of the revolt? The Dnipro River runs through the heart of Ukraine, and within two weeks the Grigorievites had taken over the middle third of that river. Roughly speaking, their power stretched 100-200km wide to the west side of the river and 50-100km to the east, in places much further. At their furthest advance, they came within 80km of Kyiv and 20 of Poltava.
There was a considerable crossover between Grigoriev’s base and Makhno’s, and as we have seen some anarchists joined the revolt. But Makhno resisted any pressure to join Grigoriev, and stayed with the Red Army, though he denounced the latter as ‘political charlatans’ and condemned the ‘feud for power’ between the two.

The Ukrainian Soviet Government
The Ukrainian Soviet government under Yuri Pyatakov, and even its more moderate successor under Christian Rakovsky, had in many ways sown the seeds of the Grigoriev revolt. There were trigger-happy Chekists gunning down innocent people, Red Army units looting villages, and there was the same grain requisitioning that had angered the Russian peasants. Pushing Ukraine over the edge were the same ultra-left policies on the land and the national question which had done so much damage in Latvia. The ‘First Universal’ complained about land nationalisation directly, with a complaint about the farmers being forced into a ‘commune.’
In an aside, it is customary at this point to lob a casual accusation that the Communists refused to cooperate with other parties, specifically the Borotbisti, who were the Ukrainian Left SRs. But Grigoriev himself was a Borotbist. His membership in the party was symptomatic of the unstable streak that was part of the Left SR DNA. It’s hardly fair to criticise the Communists for cooperating with a Borotbist and in the same breath to criticise them for not cooperating with the Borotbisti.[v]
It is tempting to present Grigoriev as a monster and to invite ridicule of his changing loyalties. Yes, as Golynkov says, he was politically illiterate and unprincipled.[vi] But a more nuanced interpretation comes from Timkov: that Grigoriev was a ‘hostage’ to his large and varied support base. ‘[I]n order to preserve his power, the chieftain had to wade into the chaos of the opinions and wishes of the peasant masses. You can say that he became their hostage.’[vii] He was, says Smele, ‘a complex and possibly unbalanced character’ and an ‘outrageous freebooter,’ but on the other hand he was ‘genuinely popular.’[viii]
His vacillations are more understandable as the vacillations of a large mass of people, not of one individual. And the wild character of these twists and turns – the turn from Rada to Hetman and back again, from Rada to Reds, from Reds to vicious pogroms – can be better understood as the throes of a mass of people in severe pain.
And we can’t blame all this pain on the mistakes of Soviet Ukraine. The Allies, the Whites, the Germans, the Rada and the Poles had all played their part as well. Further, regardless of specific mistakes or crimes by this or that force, the Grigoriev revolt was an outbreak of rage against the intolerable burdens which the Civil War had placed on rural communities in Ukraine. Partisan armies would have revolted against whoever was in charge, and later did revolt en masse against the Whites.
The Grigoriev revolt was a severe trial for the Ukrainian Red Army. As we have seen, this army was in a shambolic state. But a force of about 20,000 Ukrainians and 10,000 Russians was quickly assembled. Officials, communist youth members and members of the Jewish Socialist Bund all volunteered.
The revolt had spread like flames on petrol, but within a few weeks it had burned itself out. On May 14th large Red forces set out from Odesa, Kyiv and Poltava. Grigoriev’s all-out advance in all directions, meanwhile, was faltering. It seemed early on that his columns were advancing and conquering at lightning speed. In fact they were dispersing in all directions and disintegrating in the vast spaces of Ukraine. One by one the Red Army re-conquered the cities Grigoriev had taken, and in a series of battles in late May he lost 8,000 killed and wounded.
Grigoriev’s army disintegrated. The 3,000 who remained loyal switched to guerrilla warfare west of the Dnipro. While the Reds could declare complete victory, other local warlords had risen up in other parts of Ukraine, and Grigoriev could still raid towns, hold up trains, destroy railways.

The Whites Attack
Meanwhile the Whites had been well-positioned in the Donbass region, and in late May they had seized their moment. The White general Mai-Maevsky himself had warned his men not to underestimate Makhno’s Revolutionary Insurgent Army of Ukraine, the army on carts under the black flag of anarchism. Their partisan tactics had run rings around the Germans and the Whites. But in late May Mai-Maevsky’s forces struck deep into Ukraine. The Whites simply cut through the Anarchists. The Black Army fled, like Grigoriev, to the western fringes of Ukraine. They had been reduced to 4,000 fighters.
Arshinov, an anarchist writing in 1923, presents this move as a stubborn fighting retreat.[ix] He claims that the Reds, by contrast, gave up Ukraine to the Whites without any fight-back at all. The first claim is probably an exaggeration, and the second is completely untrue. Trotsky’s armoured train rolled into the Mikolayiv-Kherson region (Trotsky’s own home turf where his dad still had a farm) and there tried to make a stand; Kharkiv was turned into a fortress; Iona Yakir led several divisions on one of those ‘Long Marches’ which so characterized the Civil War – a 300-mile fighting retreat which succeeded in preserving large forces from destruction.
The failure of Makhno’s Revolutionary Insurgent Army of Ukraine requires explanation. The Black Army was a partisan army, its military doctrine an extension of its political philosophy. There was no contradiction between Mai-Maevsky’s appreciation of its strengths and the ease with which the same general scattered it. Its strength lay in raids and mobility; it was utterly incapable of holding a line against a determined advance. At the very least this defeat represented a political and military failure for the Anarchists. For Moscow, it was nothing less than treachery, and Makhno was outlawed.
Warlords in Exile
West Ukraine was getting crowded with the remnants of defeated armies. The Anarchists were pursued there by the General Shkuro, a cunning and merciless Kuban Cossack whose personal bodyguard were known as the ‘Wolf Hundred.’
To survive the onslaught of the White Wolves, the Anarchists made a tactical alliance with the Rada forces of Semyon Petlyura who, like themselves and Grigoriev, had ended up west of the Dnipro. The alliance was short-lived. Arshinov says the Ukrainian Nationalists soon betrayed them, a development which all parties had anticipated.
Next Grigoriev came knocking on Makhno’s door. Though Makhno had previously condemned Grigoriev and his pogroms, he agreed to cooperate pending an investigation. They fought side-by-side for three weeks against the Reds.
Grigoriev, Makhno and other Ukrainian partisans – reportedly 20,000 in all[x] – gathered for a great congress on July 27th in a village near Oleksandriya. The supposed aim of this peasant congress was to unite an anti-Bolshevik army.

There are different versions of what happened next, which you can follow up and tease out in the sources. Here is my composite sketch:
The Grigoriev forces were camped outside the village, but the village itself was occupied by Makhno’s forces, the lanes dominated by his tachankas, machine-gun carts.
At the congress, the Makhnovist Chubenko stood up at the podium and denounced Grigoriev as a murderer of Jews and a hireling of the Whites. Grigoriev denied the charges and reached for one of his Mauser semi-automatic pistols. But he realized he was surrounded by armed anarchists. He placed the Mauser in the back of his boot and fled from the scene, intending to make an appeal to the village council. But he found Makhno and his lieutenants waiting for him at the house ofthe village council. Chubenko arrived and a heated argument began.
Some days before, the anarchists had captured some White officers who had letters addressed to Grigoriev. It was obvious from the letters that the ataman was planning to join with Denikin. Remember I mentioned Iona Yakir and his fighting retreat across Ukraine? It appears Shkuro and Grigoriev were planning together to catch and destroy the retreating Reds. The anarchists shot the captured White officers and kept this intel to themselves, for the time being. Now, at the congress of July 27th, they revealed it before 20,000 partisans.
Chubenko told the Soviet security forces later:
‘Grigoryev began to deny it, and I answered him: “And who and to whom did the officers whom Makhno shot come?”
‘As soon as I said this, Grigoriev grabbed the revolver, but I, being ready, shot point-blank at him.’
Grigoriev called to Makhno by his nickname: “Oh, father, father!”
‘Makhno shouted: “Beat the ataman!”
‘Grigoriev ran out of the room, and I followed him and shot him in the back all the time. He jumped out into the yard and fell. That’s when I finished him off.’
By other accounts, such chaos ensued when Grigoriev fled, with people running in all directions, that it was impossible to see who fired the fatal shot.
Makhno and his men shot down Grigoriev’s bodyguard, then went around the village to kill the ataman’s head honchos.
‘That was the sort of treatment I always reserved,’ Makhno later wrote, ‘for those who had carried out pogroms or were in the throes of preparing them.’
But why did the Anarchists ever collaborate with these pogromists in the first place? Arshinov explains that many of the mass following Grigoriev were genuine revolutionaries, who must be won over. The July 27th congress was in fact an elaborate trap for Grigoriev. It is even rumoured that someone had secretly emptied the bullets out of the ataman’s Mauser.
The Anarchists got what they wanted: the leadership of Grigoriev’s band was wiped out, but the rank-and-file joined the Black Army.
Another rumour has it that the gold reserves of the Odesa State Bank had been in Grigoriev’s train, and that Makhno’s men immediately rode out to seize it, then buried the gold a month later. The place where they are supposed to have buried the gold is near Kherson, not far from the frontline in the current war at the time of writing. If there is any gold around there, it’s under water as well as earth. Since the 1950s the area has been flooded by the Khakovsky reservoir. Maybe someone reading this will go on a mission to the heart of a warzone to look for Makhno’s Gold.
The Fall of Soviet Ukraine
That summer, Soviet Ukraine collapsed. In August, two weeks after Trotsky recorded that half of Red Army soldiers in Ukraine had no boots or underwear, Kyiv fell to the Whites.[xi] A number of factors which we have dealt with in the last few episodescame together to produce this collapse. The Don Cossack revolt in neighbouring South Russia, the pressure from Kolchak’s Spring Offensive, the Grigoriev revolt and the flight of the Anarchists all weakened the Red southern and Ukraine fronts. This set the stage for the defining campaign of the whole Civil War: Denikin’s march on Moscow.
Go to Revolution Under Siege Archive
[i] Serge, Conquered City, p 99
[ii] SA Smith, Russia in Revolution, p 186
[iii] Savchenko, ‘Ataman of Pogroms Grigoriev’, http://militera.lib.ru/bio/savchenko/04.html/index.html. Most of my information comes from this long and remarkable essay. That, unless otherwise stated, is generally the source for whatever detail or quote you may want to follow up.
[iv] From a source quoted on the blog of Alexandria Cossacks: https://kozactvo-jimdofree-com.translate.goog/%D1%83%D0%B2%D1%96%D1%87%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%BC%D0%BE-%D0%BF%D0%B0%D0%BC-%D1%8F%D1%82%D1%8C-%D0%BE%D1%82%D0%B0%D0%BC%D0%B0%D0%BD%D0%B0/?_x_tr_sl=auto&_x_tr_tl=en&_x_tr_hl=en&_x_tr_pto=wapp
[v] On the Borotbisti more generally, my sources offer a sliding scale of sweeping statements. Supposedly the Communists merged with the Borotbisti, but also they banned them; they also, it seems, cooperated with them, all the while completely refusing to cooperate with them. I can only throw my hands up. Of course historians are supposed to summarise, employing their own interpretations. But in this case the same set of data produces completely contradictory interpretations. See EH Carr and SA Smith.
[vi] David Golynkov, quoted in https://kozactvo-jimdofree-com.translate.goog/%D1%83%D0%B2%D1%96%D1%87%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%BC%D0%BE-%D0%BF%D0%B0%D0%BC-%D1%8F%D1%82%D1%8C-%D0%BE%D1%82%D0%B0%D0%BC%D0%B0%D0%BD%D0%B0/?_x_tr_sl=auto&_x_tr_tl=en&_x_tr_hl=en&_x_tr_pto=wapp
[vii] Oleg Timkov, ‘Ataman Grigoriev: Truth and Fiction.’ https://kozactvo-jimdofree-com.translate.goog/%D1%83%D0%B2%D1%96%D1%87%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%BC%D0%BE-%D0%BF%D0%B0%D0%BC-%D1%8F%D1%82%D1%8C-%D0%BE%D1%82%D0%B0%D0%BC%D0%B0%D0%BD%D0%B0/?_x_tr_sl=auto&_x_tr_tl=en&_x_tr_hl=en&_x_tr_pto=wapp
[viii] Smele, 98, 102
[ix] Arshinov, https://libcom.org/library/chapter-07-long-retreat-makhnovists-their-victory-execution-grigorev-battle-peregonovka-
[x] Arshinov
[xi] Deutscher, p 364
New Podcast Episodes
I’m not just putting out the new series of Revolution Under Siege as a fully voiced podcast – I am re-releasing Series 1, updated, edited, expanded, and read by a human voice.
Here (and also on Youtube and Spotify) is Episode 1:
‘Warlords of Siberia’ is now live as a podcast!
The podcast is back, continuing the audio version of Revolution Under Siege. This time, no automated voice: I’m narrating it myself. Available on Google Podcasts, Spotify, and soon Youtube.
Race in Middle Earth
This bit wasn’t in the books.
Neither was this.
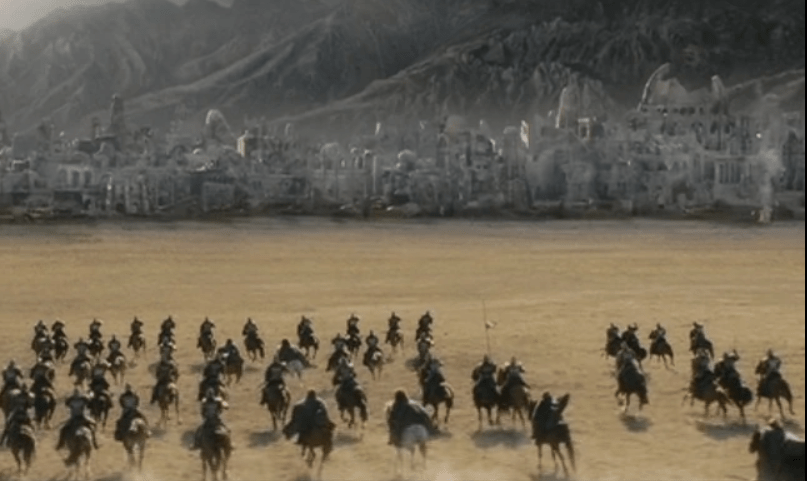

Or this, or this, or this.
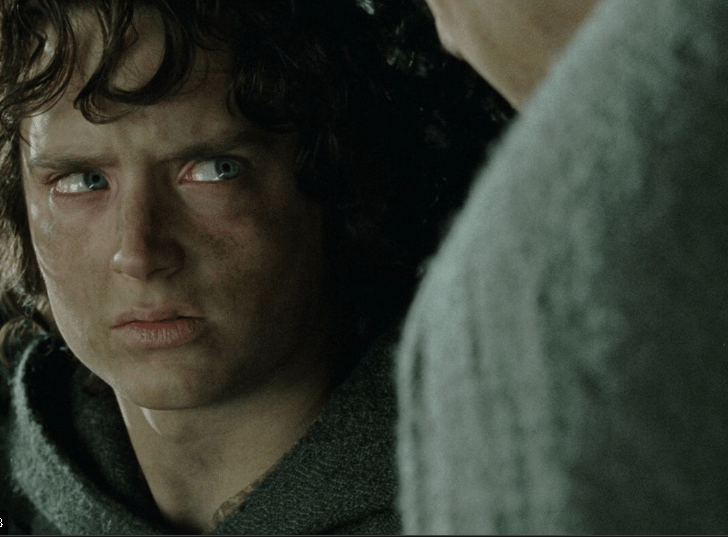


Or Legolas being a ninja, or jokes about ‘dwarf-tossing.’
In the books, there’s an incident where an evil oak tree eats several hobbits. They left that bit out. They cut Tom Bombadil, Goldberry, the Old Forest and the Barrow-Wights. Twenty years pass between the birthday and the big quest. Frodo is 50. They compressed all that just a little.
They cut the hobbits singing in the bath. In fact they cut nearly all the songs, and most of the twee hobbit banter.
They dramatically simplified the big battles, and dramatically expanded the smaller-scale fights. They added little side-adventures and contrived arguments.
They turned ‘the fellowship ran down a flight of stairs’ into this.

And nobody really minded. It was mostly great.
Now,
Take a deep breath.
Because in 2022, in the TV show Rings of Power,
They gave speaking parts to 3 or 4 black actors,
…and suddenly a lot of people on the internet were very worried about ‘staying true to Tolkien’s vision.’
Funny how that was the deal-breaker!
Not this,
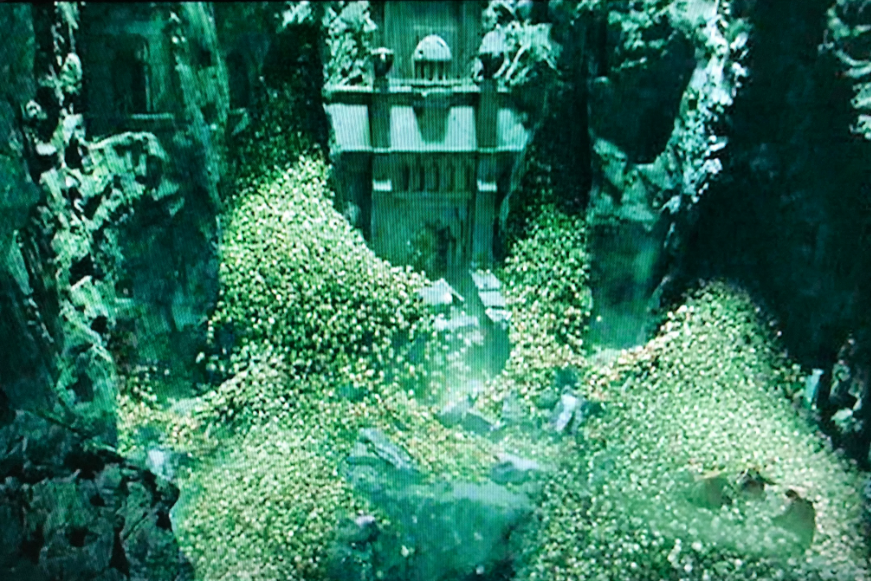

or this,

or this,

or this.
A screen adaptation that was ‘true to the spirit of Tolkien’ would have a lot more sing-songs in the bath, chipper hiking dialogue and obscure melancholy poems. The camera would linger for hours on trees and shrubs.
There’s every reason to have a diverse cast in Middle Earth. Tolkien described characters as ‘dark’ or ‘ swarthy’ in almost every chapter (good guys are usually dark, bad guys are swarthy. And yes, they’re all guys).
And if, just for the sake of argument, he did write, ‘by the way, categorically, none of these people were black’, why should we care 70 years later? Why would you care about skin pigment, if you don’t care about the scouring of the shire, the Dúnadain, Elladan and Elrohir, Prince Imrahil, Ioreth, Erkenbrand, Ghan-Buri-Ghan, the Dunlendings..?
By the way, Tolkien was sometimes racially insensitive in his writing. There are a few features and examples you can point to. There is a preoccupation with heredity, and there is a vile phrase in Book V Chapter VI. Yes: I’m sure you’re shocked to learn that an aging English Catholic professor who was born in South Africa and wrote in the 1930s to the 1950s was sometimes racially insensitive. Though at times he was surprisingly OK.
(Those Peter Jackson movies are actually dodgier on race for their time than Tolkien was for his time).
But that is not really a ‘gotcha’ for either side in these online debates.
Because when you adapt something, you make a choice about what to focus on. With Tolkien, there are themes like compassion, redemption, comradeship, self-sacrifice in struggle, and humble people rising up to change the world; and features like invented languages and histories, melancholy hints of a deep past, tense chases and battles, fantastical creatures and places.
Then there’s the ring, which poses the question of whether you would really have the integrity to destroy some great source of evil.
The movies nailed a few of those things, and that is why nobody really minded about the skull avalanche.
You could focus on some of those things, or you could make a fetish of skin colour, as if the Lord of the Rings was just a more upmarket version of 300. Then you would be putting a minor and unattractive feature of Tolkien’s writing up on a pedestal. You shouldn’t worship Tolkien, but if you insist on it, don’t be worshipping his backside.
And don’t be a racist, but if you insist on it, you’re not fooling anyone by pretending it’s about pious respect for a mid-century Oxford academic. If he could see us, or any of the screen adaptations, he’d tell us all where to get off.
How Dune gets away with it
When it was briefly mentioned on The Mindy Project, it was described as (something like) ‘That book that every guy loves for some reason.’ I read Dune at age 15. The years passed and I forgot some of the details of the story, but it held on in some remote sietch in the back of my mind, from which echoed phrases like Gom Jabbar, Muad’Dib, Kwisatz Haderach; mantras like ‘Fear is the mind-killer’ and ‘Who controls the spice controls the universe.’ The recent film captured some of that hypnotic power, and gave me an urge to visit that strange place again.
Re-reading it was a trip. Here are some things that struck me. In each case I was left wondering, ‘How does the novel get away with that?’
There is no scene of space travel in Dune. A chapter on planet Caladan ends; the next chapter begins with the characters literally unpacking their bags on planet Arrakis. The author Frank Herbert tells us that the Guild of Navigators have a monopoly on space travel, but he is not interested in exploring the technical details. He is more interested in the Guild as a political force. Therefore, unlike both of the movie versions, the space travel happens off-screen. It’s a bold move but it works. It brings focus to the story.

Dune’s rich and strange world
In the early pages we are immersed in a kind of Renaissance space feudalism. It’s all nobles having conversations in palaces; it really shouldn’t be so interesting. I don’t think space capitalism, let alone space feudalism, is plausible. There are books I’ve abandoned because there were too many nobles, too many palaces. But somehow Dune gets away with it. It confronts us with a world that runs on its own rules, and doesn’t care what we think of it. Its people are medieval in outlook, and they don’t make any effort to relate to us on our terms. Not only do these people all do drugs, drugs are at the very the centre of their society. They have slaves, they hold entire planets as fiefs and some of them have psychic powers.
In short, Herbert doesn’t try to meet us half-way. We must either dismount from the great sandworm that is this book, and watch it slither away into the distance wondering to what fascinating places it might be going, or else cling to it stubbornly in spite of its efforts to shake us off.
By the way, I was converted to the idea of space feudalism being plausible. Humanity expanded across the stars, but suffered some kind of social and cultural catastrophe as a result. Their machines advanced to the point of being dangerous, so they waged war on the machines in the Butlerian Jihad. Feudalism didn’t bring humanity to the stars; humanity, having reached the stars through some advanced social system, reverted to feudalism, a feudalism modified with the remnants of the technology built up in ancient times.
Foreshadowing
But I wouldn’t have read on for long enough to care about the Butlerian Jihad unless the foreshadowing was laid on thick. The switches between different characters and their points of view, the dense undergrowth of exposition – these are not fashionable in sci-fi/ fantasy writing today. But anyone who notices these unfashionable features and concludes that they are dealing with a clumsily-written book is mistaken.
When we ‘observe the plans within plans within plans’ we begin to wonder how these plans (within plans within plans) will work out. The story does not go from A to Z, from safety to danger. It goes from Y to Z, from less extreme danger to more extreme danger. We know the Harkonnens are going to attack. The Atreides know it. If they didn’t, the book and its sympathetic characters would be very irritating. We know Yueh is a traitor; if we didn’t, the revelation would be a pretty limp and predictable twist. We are not waiting to see if this Jenga tower will come down. We are waiting to see how.
While we are waiting for the Harkonnens to strike, we get sucked into the Duke’s administrative and political problems in a way that lulls and distracts us.
The writing and worldbuilding are open to criticism in places. I didn’t like how squeaky-clean and wholesome the Atreides were. ‘Good nobles’ vs ‘ bad nobles’ – come on. They’re an unelected ruling class who think they’re better than us. They’re all degrees of bad.
There’s a whole double-bluff intrigue where the Duke is pretending to be suspicious of Jessica. This is a tedious sub-plot, totally far-fetched. It’s just conflict for the sake of conflict. The book would be better without it. The mentat Thufeir Hawat is closely connected with this plot, but all in all I don’t see what he brings to the table. I think the book would pack a heavier punch if this sub-plot was gone and this character stripped back 90% or so.
Phallic sandworms
Paul is 15 but completely devoid of horniness or sexual neuroses; in the banquet scene, an attempt to seduce him falls flat. This is no doubt because of his Bene Gesserit training. But the repressed sexuality is central to the story. It’s more obvious to my grown-up mind that the sandworms are basically big dicks. And to paraphrase the book, who controls the big dicks controls the big dick energy. After Paul learns to harness and steer the big dicks, the climax of the story soon follows. Sorry for saying climax.
How does Frank Herbert get away with this insane sexual imagery? It’s even more obvious than King Solomon’s Mines. But it works because the sandworms work on their own terms. Arrakis without them wouldn’t be the same. Herbert doesn’t give a damn about space travel, but he cares about ecology. He reveals how this ecosystem works, and it is not a lecture we endure but a story mystery that is very satisfying to engage with and to solve.
Dune’s rich and strange hero
Speaking of Paul, even as a young reader I never quite liked him, and I never thought he was a good person. I rooted for him, and was invested in him. But I didn’t like him. He wrestles with his ‘terrible purpose’ and his visions of jihad for most of the story. As we read on, it becomes clear that is the story about the rise of a vast and terrible historical figure. It’s visible from the start, but the shock of the Harkonnen coup shakes something loose in him. As readers we come to respect the Fremen, but Paul is deceiving and manipulating them. Near the end (page 504) Gurney reproaches him when he reveals that he doesn’t really care about those killed in the final battle. He doesn’t care much about his murdered son either. And around the same time he finally embraces his ‘terrible purpose’ of galaxy-wide jihad; in his view there is no other way to cleanse the stagnant social order. The upheaval of the jihad will put a mixing spoon into the galactic gene pool and give it an almighty stir. This is the way he sees the world.
The unsettling presence of Paul’s little sister Alia is significant; he is only a little bit less weird than she is.
I haven’t read the sequels; I have been discouraged by some who have. What’s more, I consider the story complete and self-contained. It’s obvious to me that Paul is on track to become a genocidal god-emperor. There are no narrative questions left to answer.
The book suggests that Herbert does hold some beliefs that are repugnant to me: in the efficacy of eugenics, and in deep, inherent differences between men and women (‘takers’ and ‘givers’). He is cynical about humanity and believes that we will always be in thrall to religions and monarchs. But it seems clear enough that Frank Herbert doesn’t approve of Paul’s ‘terrible purpose’ or of the Bene Gesserit and their biological intrigues.
Atreides of Arabia
The ‘white saviour’ stuff is pretty blatant; Paul joins the Fremen and two years later has risen to be their messiah. This clearly takes inspiration from Lawrence of Arabia, and went on to inform Jon and the Wildlings, Dany and the Dothraki, etc.
With the Fremen, the Muslim coding is not just heavy but overwhelming. I didn’t see any problem with this when I was 15. But there was something more positive that I didn’t see either: that this is a text about the anti-colonial revolutions of the 1950s and 1960s. The Muslim stuff could be read as a tribute (perhaps a clumsy one) to the anti-colonial struggles of the Arabs, the Algerians, the Libyans. In fact the wikipedia page tells me it was also inspired by struggles of Caucasian Muslims against Tsarist Russia (hence, no doubt, the presence of a baddie named Baron Vladimir). The new film version appears to be leaning into this reading.
Conclusion
As an experiment, try to describe Dune in bald terms. It’s about a teenager who vanquishes his enemies and becomes emperor of the galaxy by convincing native people that he’s their god and by harnessing the power of huge phallic monsters.
When you put it like that, it actually sounds embarrassing.
What rescues Dune from being ‘That book that every guy loves for some reason?’ What raises Dune above the level of a basic power fantasy?
First, the world and the hero are so strange. Neither invites you in. You are forced to approach as a stranger. Paul is not the avatar for your fantasies; you end up walking many miles in his stillsuit, but you are never at all comfortable in it.
Second, it’s primarily a story about ecology and religion, not violence. It’s a story that forces us to pay attention to things we take for granted in life, such as water and faith. The indigenous people, taken for granted above all others, turn out to be the key not just to Arrakis but to the universe. It’s a book that humbles the reader, that confronts the reader with vast superhuman forces.
Last, it forces to reader to consider the cost of power. The more Paul masters these forces, the more alienated we are from him as a character. The Fremen are liberated, so it’s a satisfying ending. The ‘plans within plans within plans’ produce the most terrible blowback – for the Emperor, for the Harkonnens, for the Bene Gesserit. But Paul has reached a place where he is both all-powerful and inhuman. The worst blowback might be for the billions of innocents who will die in his jihad.
Everything feels earned. It feels earned because the desert exacts a terrible price for every blessing it gives, and there are no happy endings in this social order.
Appendix:
A note on Dune and videogames.
Dune 2 was the first strategy game, and it adapted straight from the novel a model of resource-collection that went on to exert a huge influence. There is a single resource, the spice, which lies on the surface of the ground. It is collected by huge harvesting vehicles. In Command and Conquer, the spice became tiberium, which has its own interesting back-story but is functionally identical, with the big harvesting vehicles and all. In the Red Alert spin-off, the spice appears in an alternate-history Cold War setting as Ore, a single one-stop-shop resource. Armies supply themselves by mining this resource on the battlefield. Helpfully, it is spread in pockets evenly across the surface of the earth from Manhattan to the Siberian taiga.
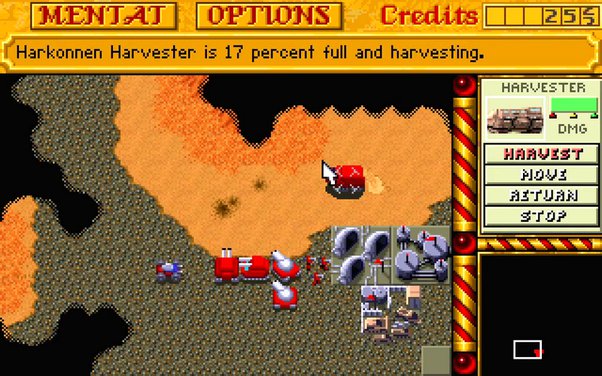

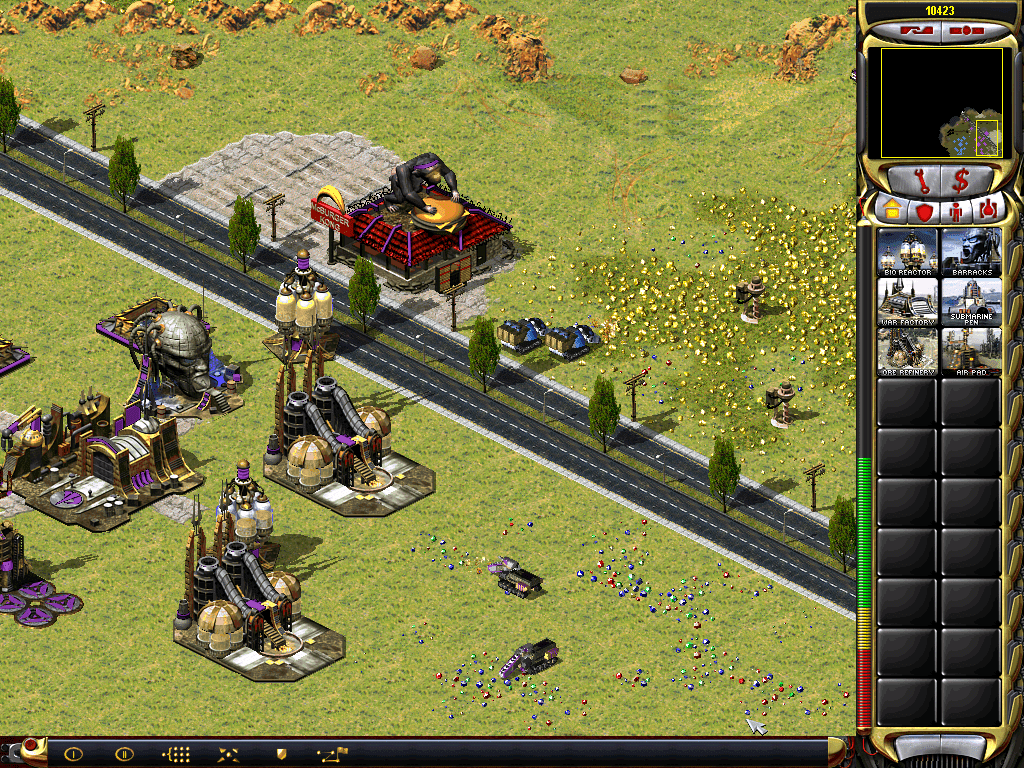
So when Frank Herbert wrote about spice-harvesting in the early 1960s, he was creating a model which videogame developers would still be using in the 21st century. It was such a useful model for gaming that the plausibility of the game world of Red Alert was stretched to the limit just to accommodate it.
Cogadh Cathartha na Spáinne – acmhainní breise
Ta mé tar éis trí nó ceithre billeog a chur leis an méid a chur mé anseo an seachtain seo chaite.